Experimental Radio Applications at the FCC
This summarizes a selection of applications for the Experimental Radio Service received by the FCC during March 2011. These are related to VHF propagation, satellite communications, TV white space, military communications, radar, software defined radio, aircraft broadband services, adaptive networks, peer-to-peer networks, intermodulation testing, unmanned aircraft systems, maritime broadband communications, border surveillance, target acquisition, and millimeter wave propagation. The applications are sorted by frequency.
- Brian D. Justin, Jr., an amateur radio operator, filed an application with exhibits for special temporary authority to operate a propagation test beacon on 70.005 MHz at Bedford, Virginia. In his application, he reports an increasing interest in trans-Atlantic VHF communications by amateur radio operators, in part because of recent changes in EU regulations. A beacon would help operators know when sporadic E propagation (E-skip) conditions were good for communications near that frequency. (E-skip is enabled by scattered regions of relatively dense ionization that develop seasonally and reflect signals up to about 150 MHz.) Today, there are beacons on 50 MHz, and FM broadcast stations act as beacons in the 100 MHz range. There’s a gap at 70 MHz; AM video carriers once served as beacons (e.g., VHF channel 4 with a video carrier at 67.25 MHz), but those have gone away with the DTV transition.
- The University of Michigan’s Professor James Cutler filed an application with exhibits for experimental license to operate communication links for the Michigan Multipurpose Minisat (M-Cubed), a small student-built satellite that will capture images of Earth and transmit them to a ground station. The satellite weighs 1.3 kg and forms a cube 10 cm on a side. The imaging system consists of a 2.0 Megapixel CMOS sensor and Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) coprocessor. The test is to prove the reliability of the radiation-hardened FPGA in the space environment and assess the performance of the processing algorithm that will resolve the images in the satellite. M-Cubed will be launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base on a Delta-II rocket in the fall of 2011. The uplink will be on 144-146 MHz. The downlink will be on 437-439 MHz using an Astrodev Li-1 radio.
- Carlson Wireless Technologies filed an application with exhibit for special temporary authority to test TV white-space radios in rural, rugged, and forested areas. Testing will take place in various areas around New England on 174-216 MHz.
- Rockwell Collins filed an application with exhibit for special temporary authority to demonstrate its FlexNet software-defined radio technology at the 2011 Coalition Warrior Interoperability Demonstration, an annual event directed by the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff that is intended to showcase new information technology. Operation will be on 245-327 MHz at Peterson Air Force Base in Colorado Springs, Colorado.
- Telephonics Corporation filed an application with exhibit for special temporary authority to test an existing 2.4 GHz ISM band product modified for operation in the 300-400 MHz military band. In addition to the change in frequency, the multiple-access method will be changed to frequency-hopping spread spectrum. The objective is to achieve superior communications in urban environments compared to 2.4 GHz operation. Testing will occur in Sterling Heights, Michigan.
- Panasonic Avionics Corp. filed an application with exhibit for special temporary authority to conduct ground testing in support of the Panasonic’s Global Communications Suite, featuring the eXConnect Ku-band aeronautical mobile-satellite service (AMSS) system, providing broadband connectivity to passengers in flight. Panasonic wants to test the potential for interference from transmitting portable electronic devices to aircraft avionics and communications. The test will use a signal generator to simulate the operation of multiple devices. Test results will be used to support certification of Panasonic’s aircraft equipment with the FAA. The tests will occur in Roswell, New Mexico on various frequencies between 410 MHz and 5.825 GHz.
- Carlson Wireless Technologies filed an application with exhibits for special temporary authority to test fixed white-space devices with attached cellular femtocells. Carlson Wireless and Vergennes Broadband are working jointly with Spectrum Bridge to investigate the applicability of white space spectrum for use in rural broadband applications, including support of femtocells. Operation will be in Vergennes, Michigan on 470-698 MHz.
- Microsoft filed an application with exhibit for special temporary authority to demonstrate interactive Xbox Live HD (1080p) video streaming over TV-band white-space spectrum during the April 11-14 NAB Show at the Las Vegas Convention Center. The demonstration was to incorporate Microsoft Research’s prototype white-spaces database, which controls white-space device access to help protect incumbents from interference. The frequency bands requested were 512-608 MHz and 614-698 MHz.
- Shared Spectrum Company filed an application with exhibit for experimental license to conduct tests as part of DARPA’s Wireless Network after Next (WNaN) program. The goal of the program is to “develop and demonstrate technologies and system concepts enabling densely deployed networks in which distributed and adaptive network operations compensate for limitations of the physical layer of the low-cost wireless nodes that comprise these networks.” Operation will be on 902-928, 2400.0-2483.5, 4400-4900, and 5650-5925 MHz in Stafford and Prince William Counties in Virginia.
- LightSquared filed an application with exhibit for experimental license to communicate with SkyTerra-1, a licensed and in-orbit satellite, and conduct a six-month test of two prototype models of Access Terminals (ATs) using the L-band spectrum coordinated for LightSquared’s satellite system. The ATs will transmit on 1626.5-1660 MHz and receive on 1525-1559 MHz. Testing will occur throughout North America.

- Lockheed Martin filed an application with exhibit for experimental license for flight tests of real-time video transmission using the company’s F-35 Joint Strike Fighter. The video source will be the F-35’s Electro Optical Targeting System (EOTS). EOTS video data will be compressed and routed to an L-3 VORTEX transmitter. The transmitted signal will be received by an L-3 ROVER 5 handheld transceiver with the video displayed on a screen in the device. Operation will be at several locations around the US on 1710-1850 and 2200-2500 MHz.
- GBL Systems filed an application with exhibit for experimental license to develop, test and validate homeland security applications based on a peer-to-peer system under development by Qualcomm. Operation will be in Camarillo, California on 1915-1920 MHz.
- Row 44 Inc. filed an application with exhibit for experimental license to conduct tests using its aeronautical-mobile satellite service (AMSS) network. The tests will use a GSM picocell connected to Row 44’s Ku-band network in a simulated aircraft cabin environment. The objective is to understand the operation of GSM devices in the on-board environment. The tests will take place in Lombard, Illinois on 1930-1990 MHz.
- L-3 Communications filed an application for special temporary authority to operate on 2025-2120 MHz at Simi Valley, California. L-3 builds antennas for satellite tracking, telemetry, and control. The company says it has been experiencing high passive intermodulation (PIM) distortion that “causes transmitter noise to bleed into the receive band.” The testing is intended to resolve this problem.
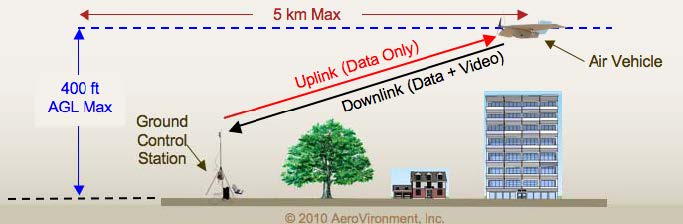
- AeroVironment Inc. filed an application with exhibits for experimental license to conduct experiments with small unmanned aircraft system (SUAS) technologies intended for use by to state and local public safety agencies. Operation is to be on 4940-4990 MHz in the Camp Roberts and Simi Valley areas of California.
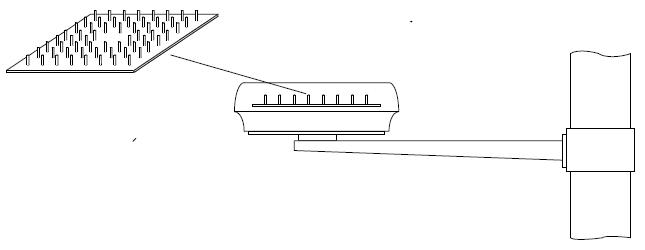
- Kongsberg Seatex AS, a Norwegian company, filed an application with exhibit for experimental license to test its Embedded Maritime Broadband Radio (EMBR) system. The system is intended to provide maritime users with reliable broadband data links using a system with no moving parts such as mechanically-steerable antennas. The system can operate at 5 Mbps when the distance between the nodes is up to 10 km. To eliminate the mechanically-steerable antenna, the system uses an electronically-steerable antenna array comprised of 60 antenna/transceiver sub-units. While there are other maritime broadband data link systems, such as those based on Wi-Fi and WiMAX, this system is said to outperform those due in part to a custom Physical Layer and Media Access Control Layer. Operation will be at 5220-5240 MHz on a route between Galveston, Texas and a Shell oil drilling rig in the Gulf of Mexico.
- Raytheon Network Centric Systems filed an application with exhibit for special temporary authority to test its Pathfinder maritime radar system in border surveillance applications. Operation will be on 9.41-9.71 GHz in McKinney and Falcon, Texas.
- SRC Inc. filed an application for special temporary authority to conduct demonstrations of the SR Hawk ground surveillance radar at Fort Benning, Georgia. Operation will be on 16.21-16.50 GHz.
- Laurel Technologies Partnership filed an application with exhibit for special temporary authority to test the operating capability of the Manportable Surveillance and Target Acquisition Radar (MSTAR) after its integration into a border and force protection ground surveillance system. The system is comprised of a trailer-mounted telescoping mast that supports a sensor package. That package includes the MSTAR radar and two video cameras (for day and night). The experiment will test and evaluate target detection and tracking capabilities of the radar and visual capabilities of the cameras once a target is acquired. Testing will be on 16.75-17.25 GHz in the Largo, Florida area.
- Samsung filed an application for special temporary authority to conduct sounding and propagation measurements on 28 GHz in Richardson, Texas. Samsung wants to better understand the outdoor mobile environment and its impact on path loss, angular spread, delay spread, and non-line-of-sight beamforming.
[cross-posted from Steve Crowley’s blog]
Previous Post